Automotive Suspension Parts: The Car's Invisible Guardians
 2025.08.22
2025.08.22
 Industry News
Industry News
Among the complex structure of a car, there's a group of components that aren't often directly noticed by the driver, yet they play a crucial role in the driving experience and safety. These are the automotive suspension parts. Like the car's invisible guardians, they work silently to ensure a smooth ride in all road conditions.
The Core Mission of the Suspension System
The automotive suspension system's primary function is to connect the vehicle's body to the wheels, transmitting forces and torques between them. It also shoulders the important task of cushioning the impact of road bumps and rapidly dampening the resulting vibrations, ensuring a smooth and stable ride. Imagine, without a suspension system, driving over potholes would be like riding on a trampoline, tossed around by the violent vibrations. This would not only destroy comfort, but also make vehicle control extremely difficult and potentially endanger driving safety.
Automotive Suspension Parts: Each with its own function
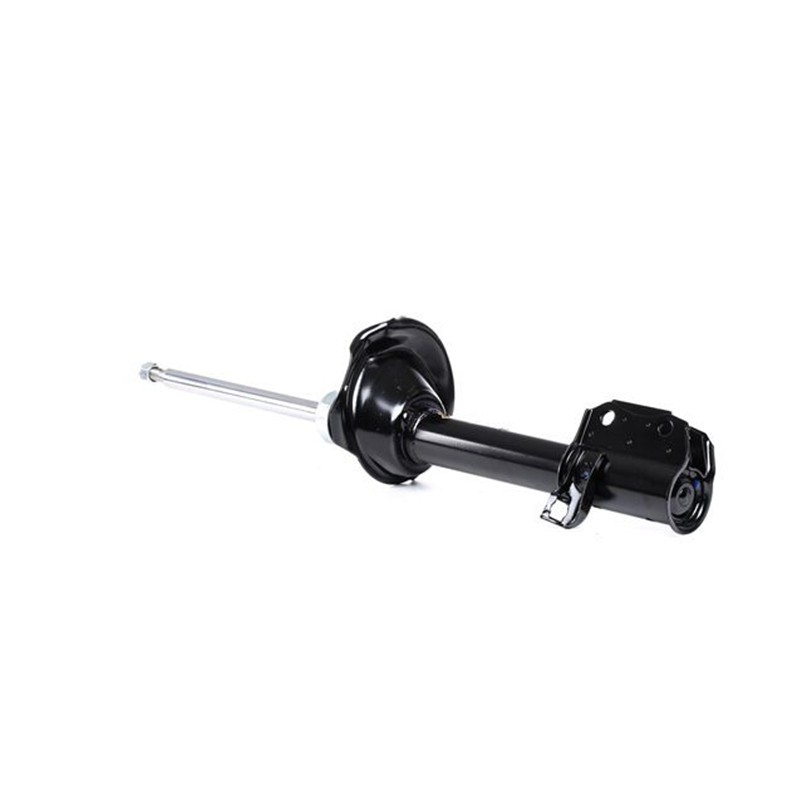
Elastic Elements: The Pioneers of Shock Absorption
Elastic elements are the first components in the suspension system to experience road impact. Common elastic elements include coil springs, leaf springs, air springs, and torsion bar springs. Coil springs are widely used in modern vehicles, especially passenger cars, due to their compact structure and minimal space requirements. They effectively absorb the energy generated by road bumps, preventing the vehicle body from vibrating significantly due to sudden impacts. Leaf springs, with their high load-bearing capacity, are highly effective in commercial vehicles such as trucks and buses. Air springs, with their adjustable stiffness and height, provide enhanced comfort and maneuverability in high-end vehicles.
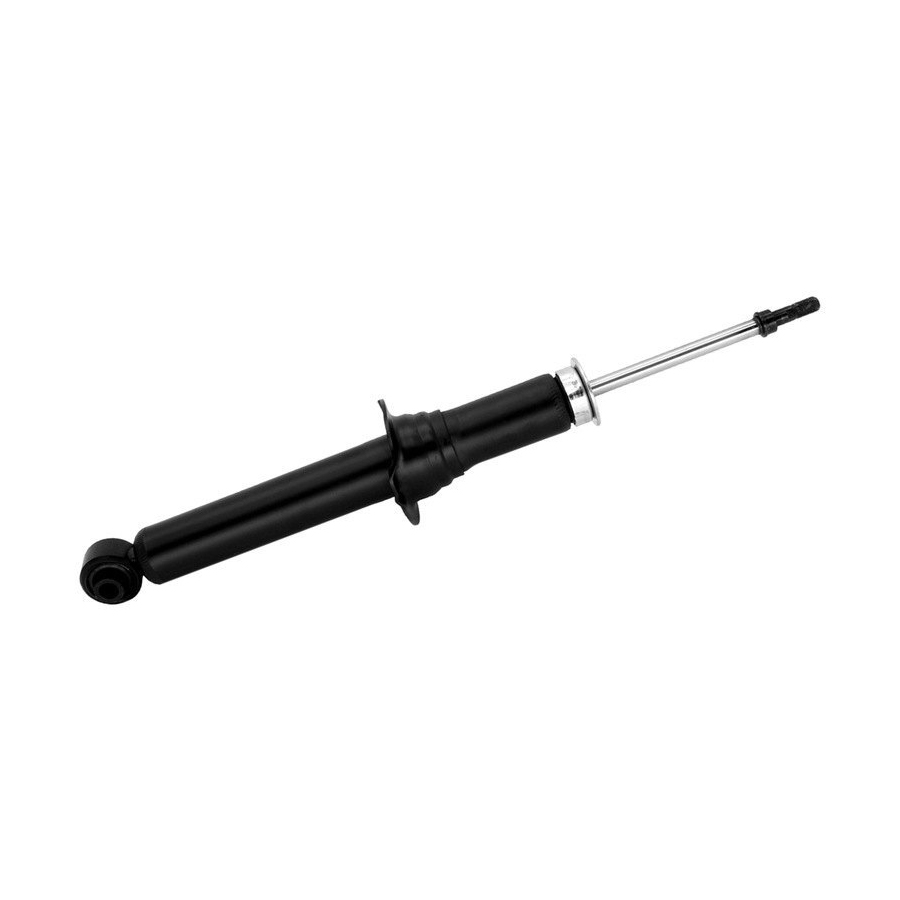
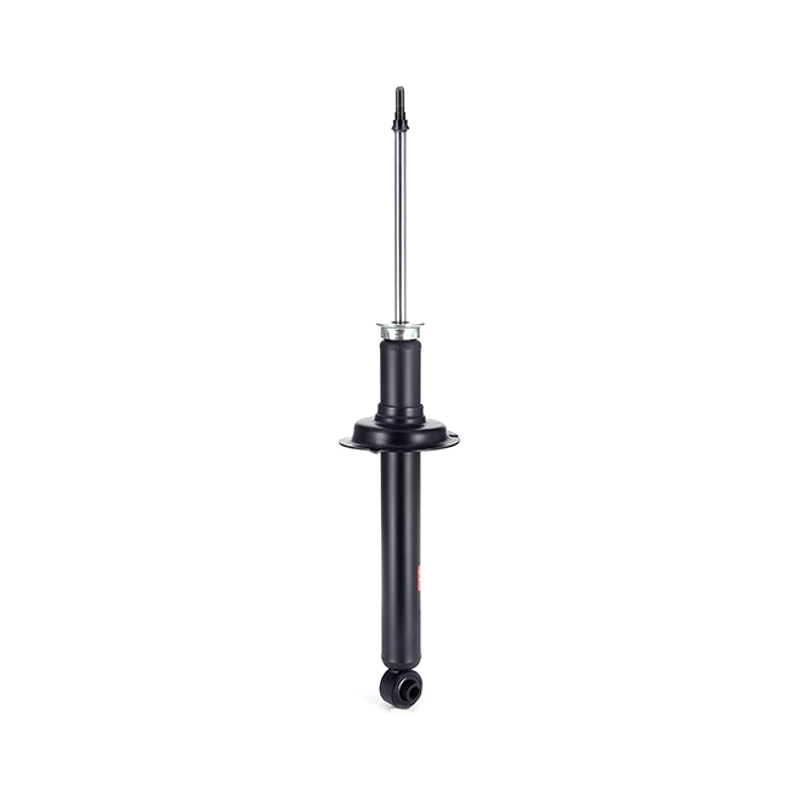
Shock absorbers: The masters of vibration control
Shock absorbers work closely with elastic elements to suppress excess vibration caused by spring rebound. When a wheel passes over a bump or pothole, the spring quickly rebounds. However, without the restraint of the shock absorber, the vehicle body would continue to sway like a runaway swing. The shock absorber's internal damping mechanism converts the kinetic energy of the spring rebound into heat and dissipates it, allowing the vehicle body to quickly regain stability. Common shock absorbers include hydraulic and pneumatic types. Hydraulic shock absorbers are the most widely used due to their mature technology and low cost. Gas-pressure shock absorbers, however, are favored by some high-performance vehicles for their quick response and efficient damping.
Guiding Mechanism: The Guide of the Wheel's Path
Guiding mechanisms are responsible for determining the wheel's trajectory relative to the vehicle body, ensuring that the wheel maintains the correct position under various driving conditions. They transmit the longitudinal and lateral forces, as well as the resulting torque, during vehicle movement. Guiding mechanisms come in various forms, such as control arms and connecting rods, which are common in independent suspension systems. Control arms connect to the vehicle body and wheels via ball joints, allowing the wheels to move up and down within a certain range while limiting their lateral and longitudinal displacement, ensuring vehicle stability. In non-independent suspension systems, the axle plays a crucial guiding role, ensuring coordinated wheel movement.
Stabilizer Bars: The Guardian Against Roll
Stabilizer bars are primarily used to reduce vehicle body roll during cornering. When a vehicle turns, the outer wheels experience increased pressure, causing the vehicle body to tilt outward. The stabilizer bar connects the left and right suspension systems. When one wheel bounces upward, the stabilizer bar generates a torsional force, pulling the other wheel upward as well, thereby reducing body roll. This ensures excellent handling and stability even when cornering at high speeds, giving the driver greater confidence.
A Clever Combination of Suspension Types and Components
Automotive suspension systems are primarily categorized as independent and non-independent. Each type has its own unique component composition and layout.
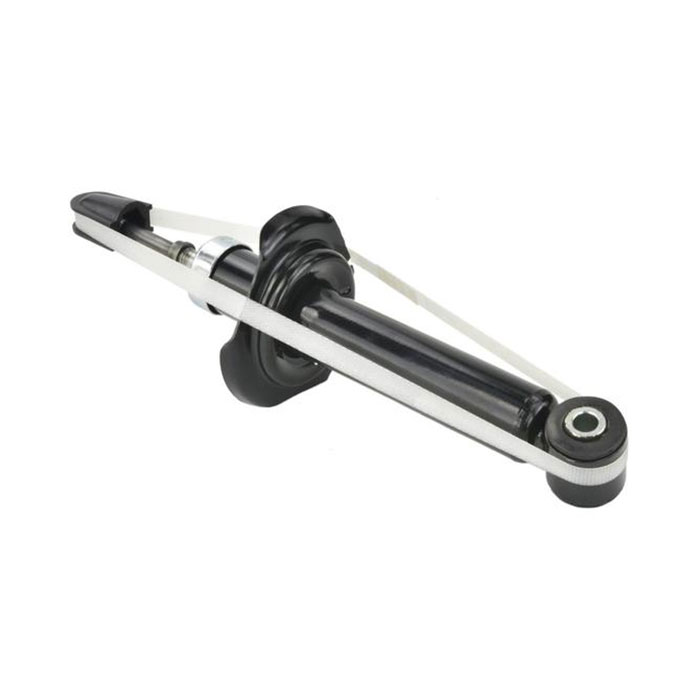
Independent Suspension: Ensuring Precise Control and a Comfortable Ride
In an independent suspension system, each wheel is connected to the vehicle body via a separate spring element, shock absorber, and guide mechanism, ensuring no interference between wheels. Common independent suspension types include McPherson, double wishbone, and multi-link. The McPherson independent suspension boasts a simple structure and compact footprint, making it a common front suspension option for front-engine, front-wheel drive vehicles. Consisting primarily of coil springs, shock absorbers, and lower control arms, it provides excellent handling while ensuring a certain level of comfort. Double-wishbone independent suspension, with its precise wheel control using two upper and lower wishbones, is widely used in high-performance sports cars and some high-end SUVs. Its excellent lateral support ensures exceptional performance during high-speed cornering. Multi-link independent suspension uses multiple links to provide comprehensive wheel restraint, enabling better adaptation to complex road conditions and providing ultimate passenger comfort. It is commonly found in the rear suspension of luxury sedans.
Non-independent suspension: A choice for load-bearing and practicality
In a non-independent suspension system, both wheels are connected by an integral axle, which is then attached to the vehicle body via an elastic suspension system. This type of suspension offers a simple structure, low cost, and high load capacity, making it commonly used in trucks, buses, and other practical vehicles. For example, leaf spring non-independent suspension utilizes leaf springs as the elastic element, offering high strength and reliability, capable of withstanding heavy loads. Torsion beam non-independent suspension, with its compact structure and minimal footprint, is commonly used in small and economy cars. It uses a torsion beam to balance wheel bouncing. While it offers slightly less comfort, it can meet basic driving needs.
The health of suspension components is crucial to driving safety.
Over long-term use, suspension components gradually wear out or become damaged due to various forces. Suspension component problems can severely impact vehicle performance. For example, aging or broken springs can cause a drop in ride height, resulting in a noticeable jerkiness and even unusual noises when driving over speed bumps or potholes. Failed shock absorbers can increase vehicle vibration, making the vehicle prone to nodding under braking, reducing stability at high speeds, and making handling more difficult. Worn ball joints and bushings in the guide mechanism can lead to wheel misalignment, resulting in deviation and abnormal tire wear. Therefore, regular inspection and maintenance of suspension components are crucial. Promptly identifying and replacing damaged components ensures optimal vehicle performance and protects the safety of the driver and passengers.
 EN
EN  English
English Español
Español








 +86-13757453333
+86-13757453333  +86-572-8355557
+86-572-8355557  Caroline@gerep.cn
Caroline@gerep.cn  No. 36, South Zhenxing Rd., Zhongguan Town, Deqing County, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China
No. 36, South Zhenxing Rd., Zhongguan Town, Deqing County, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China 